
The crosses indicate the magnetic field is acting into the plane of the diagram. The diagram below shows a conductor of length $l$ which is part of a complete circuit cutting through the lines of a magnetic field of flux density $B$. If the wire is moved parallel to the field lines, no current flows.įleming's right hand rule shows how the applied force, field lines and induced current all act perpendicular to each other.įaraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction


With a generator, a force is applied so the wire and magnet move relative to each other which induces a current in the wire: With the motor effect, a current is applied which induces a force on the coil, making it spin. The work done by the cyclist in spinning the magnet is equal to the energy transferred to the lamp, assuming no energy is lost to the surroundings through friction or resistance. When a magnet in a dynamo spins, a current is induced, lighting a lamp. In most power stations, turbines rotate coils between a magnet which induces a current. In a complete circuit this induces a current which can be used for:
EMF FORMULA MAGNETIC FLUX FREE
When equilibrium exists, the magnetic force, F=qvB, will balance the electric force, F=qE, such that a free charge in the bar will feel no net force.Electromagnetic induction occurs when a conductor cuts across the field lines of a magnetic field, inducing an emf in the wire. The separated charges will create an electric field which will tend to pull the charges back together. It will tend to move negative charge to one end, and leave the other end of the bar with a net positive charge. This force will act on free charges in the conductor.
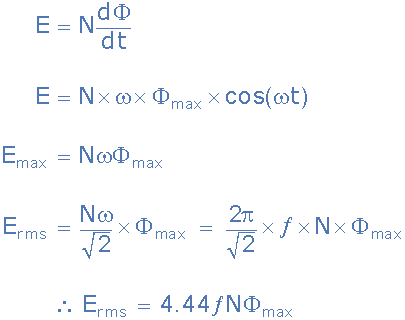
The change in the flux is thus equal to its original value,į i = B A cos q = (0.15T) p(0.12m)² = 6.8×10 -3Tm²Įmf = N ( DF / Dt) = (6.8×10 -3Tm²)/(0.20s) = 3.4×10 -2V = 34mV.Īn interesting application of Faraday's law is to produce an emf via motion of the conductor.Īs a simple example, let's consider a conducting bar moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field with constant velocity v.įor this first look, we have just a bar, not a complete conducting loop, and we will consider what happens using just the force on a moving charge, F = qvBsin q. When the loop is stretched so that its area is zero, the flux through the loop is zero. This is a case where the change in flux is caused by a change in the area of the loop.īoth the magnetic field and the angle q remain constant. If it takes 0.20s to close the loop, find the magnitude of the average induced emf in it during this time. The loop is grasped at points A and B and stretched until it closes. The flexible loop in Figure P20.10 has a radius of 12cm and is in a magnetic field of strength 0.15T. Magnetic flux is defined in a similar manner to electric flux.įor a loop of wire with area A, in a magnetic field, B, the magnetic flux, F is given by: We quantify the change in terms of magnetic flux.
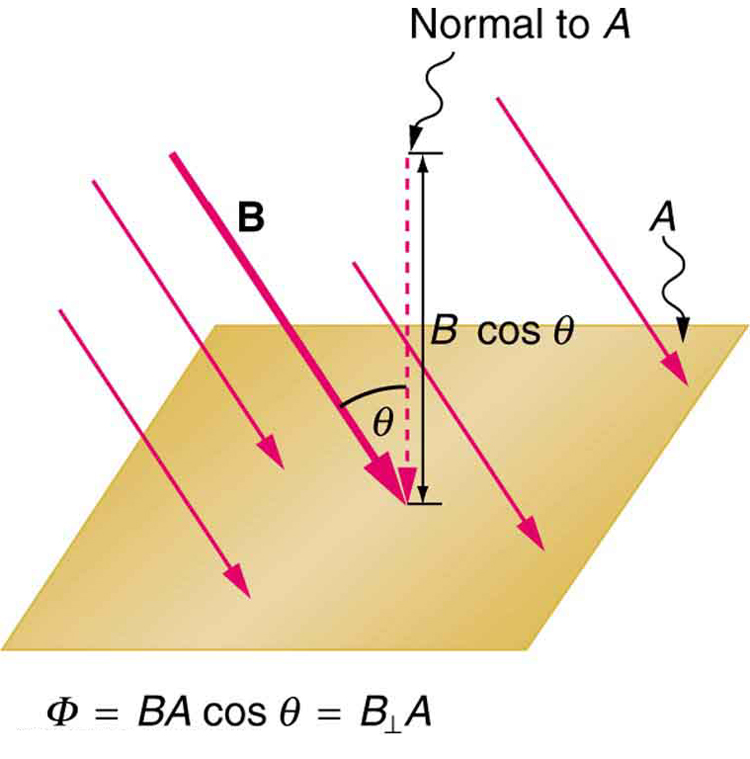
Magnetic flux will play an important role throughout this chapter.Įxperiments in the 19th century showed that a changing magnetic field can produce an emf. In this chapter, we make that connection, seeing how a magnetic field can produce a potential difference. We have seen that a magnetic field exerts a force on a wire carrying a current, and that a wire carrying a current generates a magnetic field.Ĭurrents are produced by electric fields, so there seems to be some connection between electricity and magnetism. repulsive when the currents are in opposite directions.attractive when the currents are in the same direction.Force Between Two Wires: F / l = m 0 I 1 I 2 / 2 p d.Torque on a Current Loop: t = B I A sin q.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
